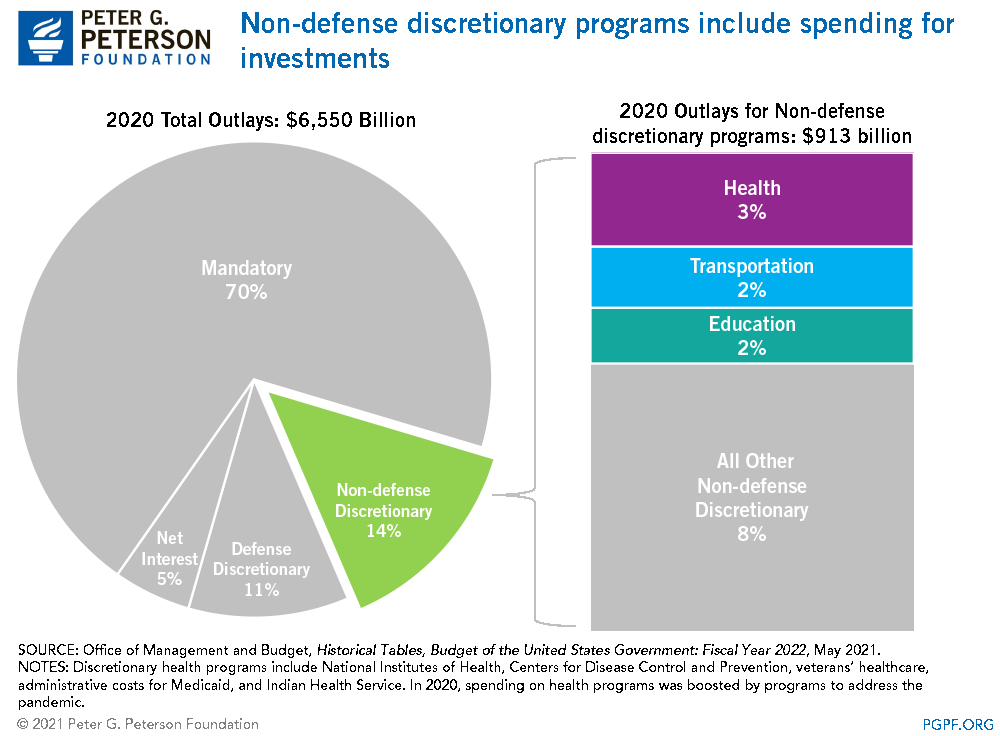
Composition of Nondefense Discretionary Spending
Nondefense discretionary spending includes many programs that could promote future economic growth.
https://www.pgpf.org/chart-archive/0021_discretionary-spending
The search found 406 results in 0.192 seconds.

Nondefense discretionary spending includes many programs that could promote future economic growth.
https://www.pgpf.org/chart-archive/0021_discretionary-spending
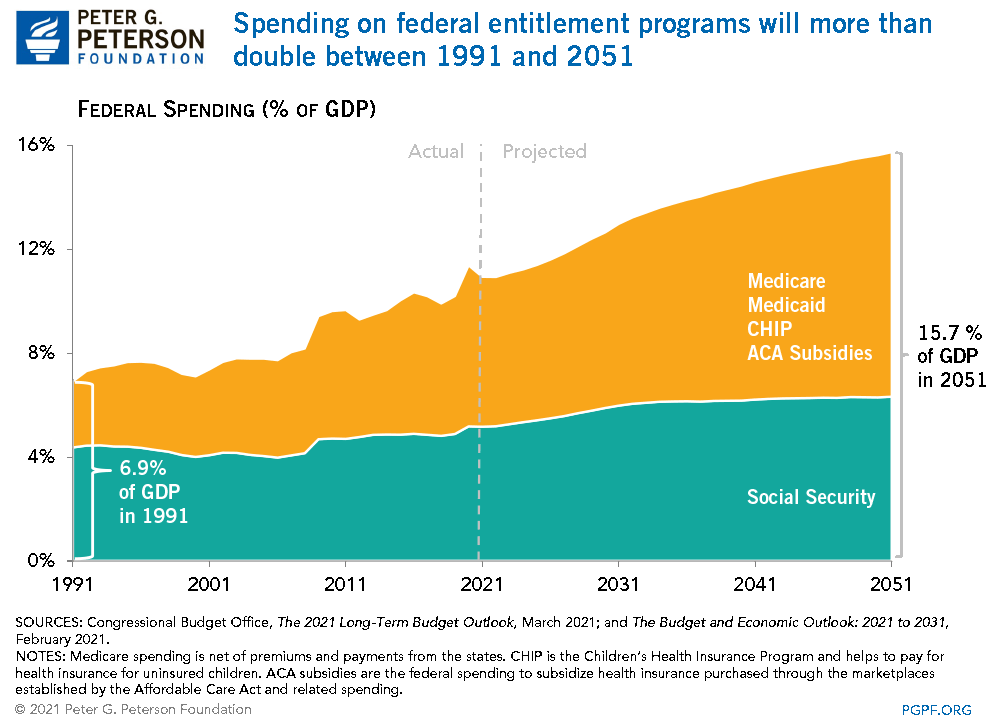
Spending on federal entitlement programs will more than double between 1991 and 2051.
https://www.pgpf.org/chart-archive/0027_entitlement-programs-proj
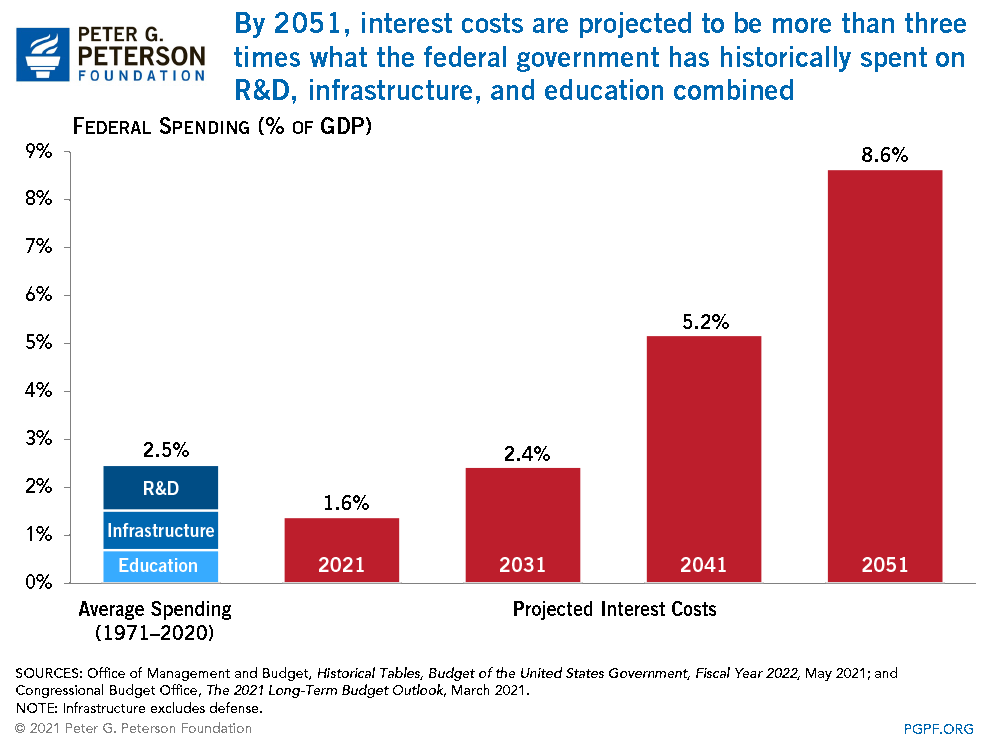
By 2051, interest costs are projected to be more than three times what the federal government has historically spent on R&D, infrastructure, and education combined.
https://www.pgpf.org/chart-archive/0005_investments_interest
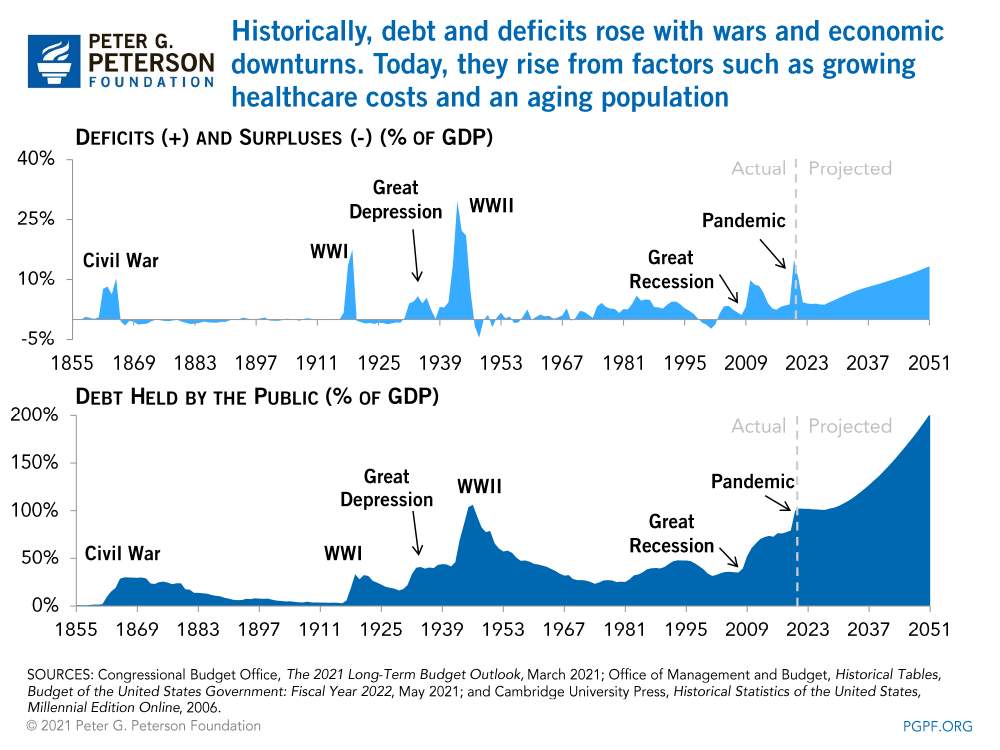
Historically, debt and deficits rose with wars and economic downturns. Today, they rise from factors such as growing healthcare costs and an aging population.

Spending on foreign affairs accounts for slightly more than 1 percent of total federal spending.
https://www.pgpf.org/chart-archive/0239_foreign_affairs_spending
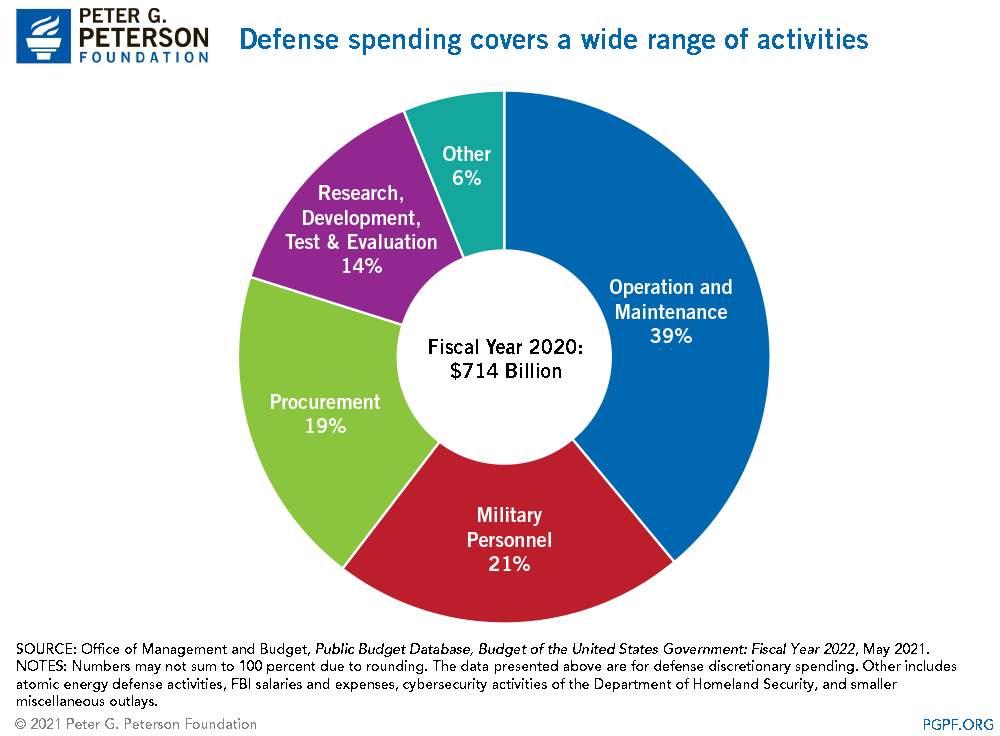
Defense spending covers a wide range of activities.
https://www.pgpf.org/chart-archive/0314_defense_spending_categories
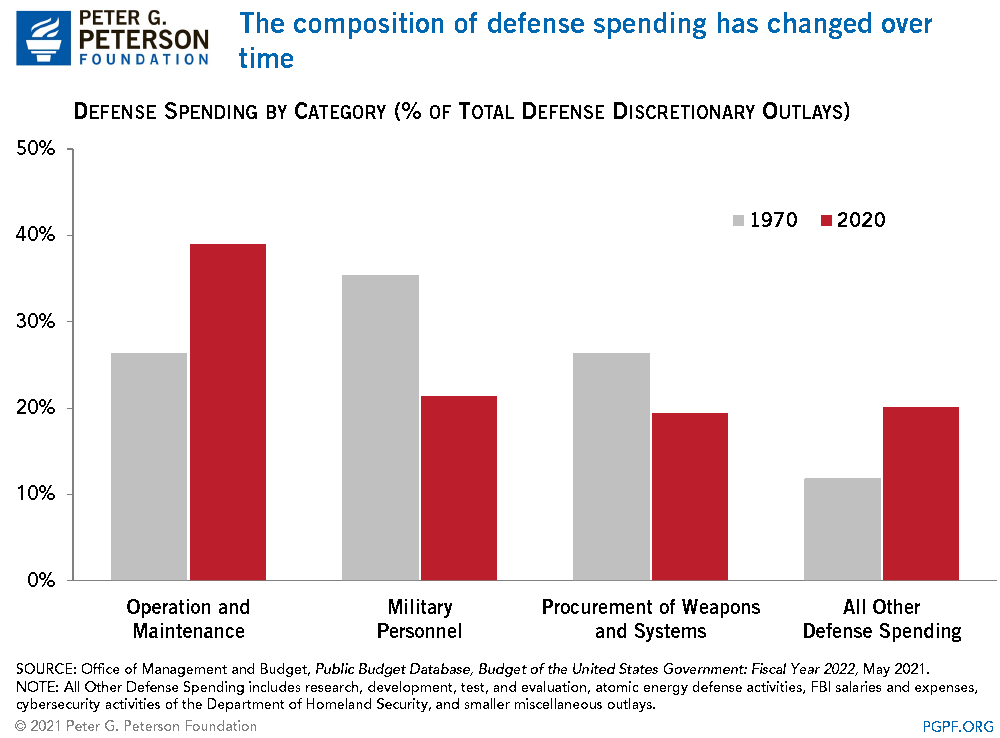
The composition of defense spending has changed over time.
https://www.pgpf.org/chart-archive/0315_defense_spending_change

Non-defense discretionary spending funds a wide range of programs
https://www.pgpf.org/chart-archive/0318_nondefense_disc_categories
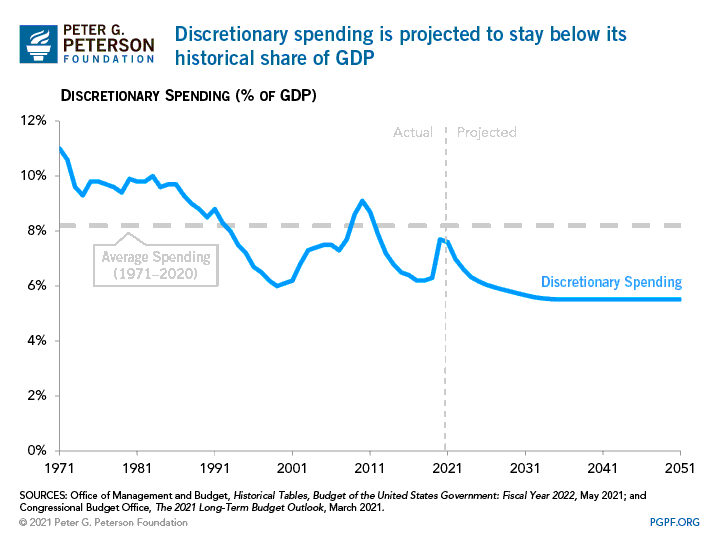
Discretionary spending is projected to stay below its historical share of GDP.
https://www.pgpf.org/chart-archive/0177_discretionary_low_levels
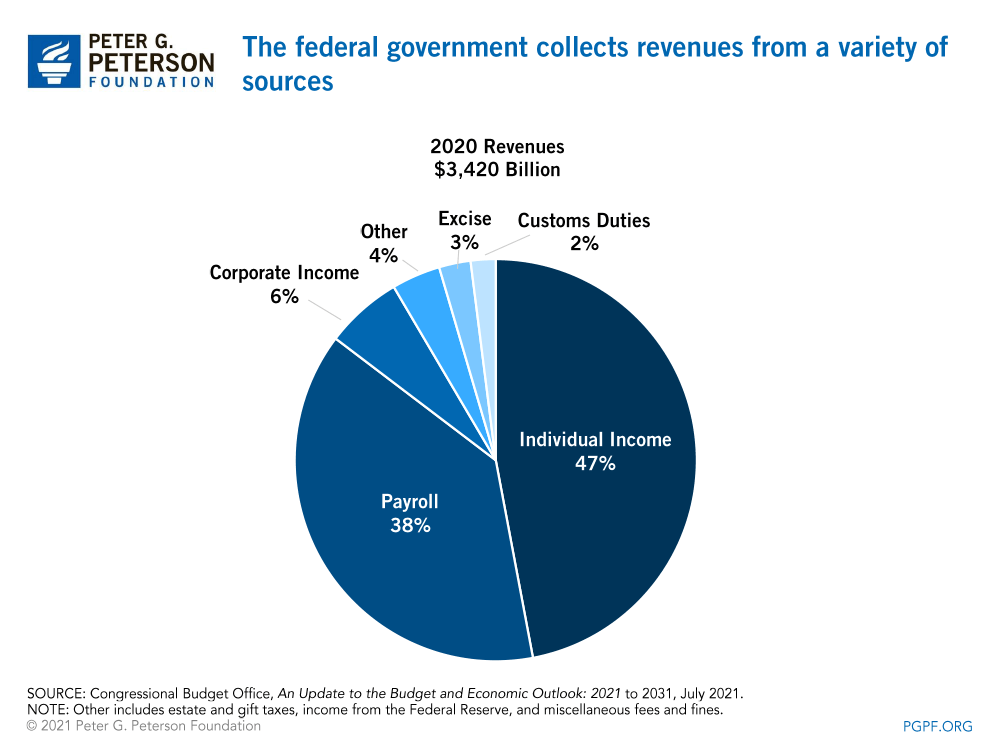
The federal government collects revenue from a variety of sources.